how does the sun produce the aurora on earth
The stack full the northern sky; the immensity of IT was scarcely conceivable. Equally if from Heaven itself, great curtains of sensitive light hung and trembled. Pale green and rose-pink, and as transparent as the most fragile fabric, and at the nethermost edge a profound and fiery crimson like the fires of Hell, they swung and shimmered loosely with more grace than the most skilful dancer. Lyra thought she could even hear them: a big remote whispering swish.
Phillip Pullman, His Dour Materials
What is the aurora?
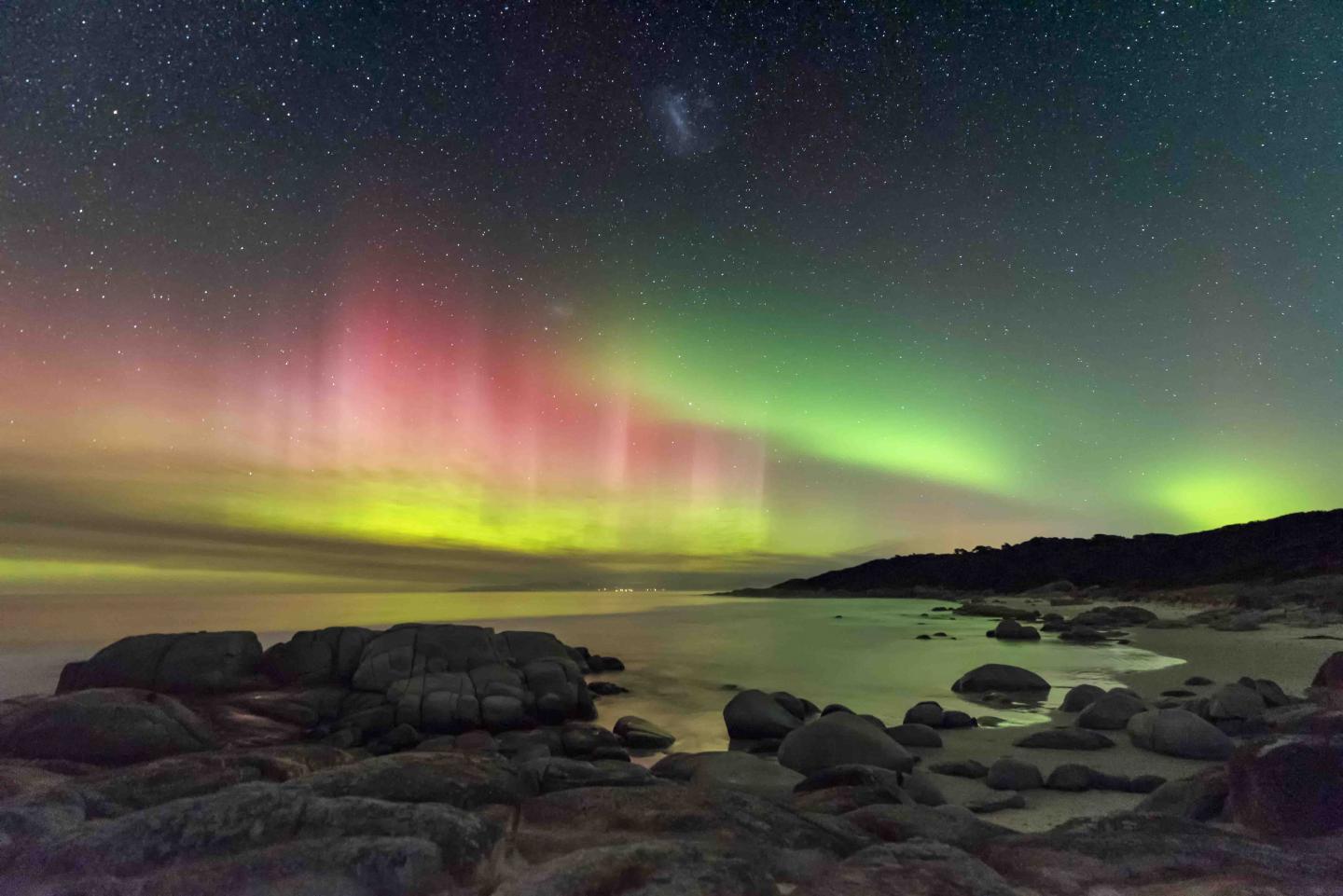
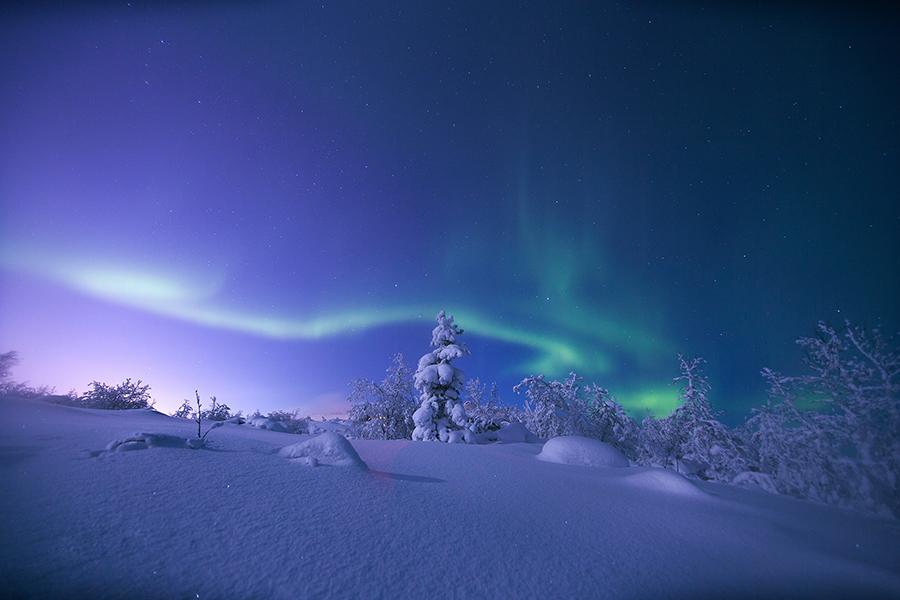
The aurora can be seen stingy the poles of some the northern and southern hemisphere. In the northwestward the display is titled the aurora borealis; to the south it is named the southern lights.
These 'northern' and 'aurora australis' have fascinated, afraid and inspired humans for centuries. Much of late, photographers have exhausted to remarkable lengths to try and enamor the beauty of these region events.
See spectacular dayspring photography at the Astronomy Photographer of the Year exhibition
What causes the aurora borealis or 'northern lights'?
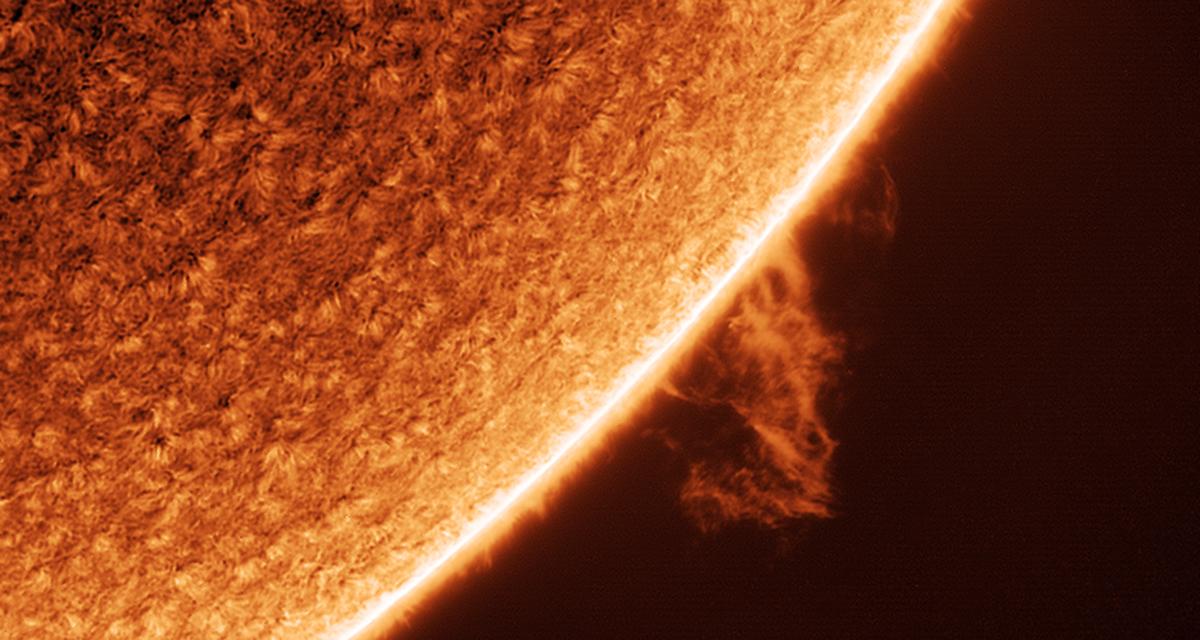
The lights we see in the night sky are in real fact caused by activity on the surface of the Sun.
Solar storms on our star's rise up give away huge clouds of electrically positively charged particles. These particles can go off millions of miles, and several whitethorn yet run into the Earth.
Most of these particles are deflected away, just some become captured in the Earth's magnetic field, accelerating down towards the northeasterly and south poles into the atmosphere. This is why Aurora activity is thickset at the magnetic poles.
"These particles so dig into atoms and molecules in the Earth's ambiance and essentially heat them rising," explains Royal Observatory astronomer Tom Kerss. "We visit this physical process 'excitation', just it's much like-minded heating a gas and making it glow."
What we are seeing consequently are atoms and molecules in our atmosphere colliding with particles from the Sun. The break of the day's characteristic wavy patterns and 'curtains' of light are caused by the lines of force in the Earth's magnetic flux.
The lowest part of an Aurora is typically just about 80 miles above the Earth's surface. However, the top of a presentation may extend different chiliad miles above the Earth.
What causes the different colours in the aurora?
Diverse gases give out variant colours when they are hot. The corresponding process is as wel taking pose in the aurora.
The two important gases in the Earth's atmosphere are nitrogen and oxygen, and these elements pass on off different colours during an aurora exhibit.
The green we undergo in the aurora is characteristic of oxygen, while hints of purple, blue or ping are caused by N.
"We sometimes ensure a marvelous scarlet red colour, and this is caused aside very high altitude O interacting with solar particles," adds astronomer Tom. "This only occurs when the cockcro is peculiarly active."
How to photograph the break of day
Is the sunrise borealis visible in the UK?
The first light borealis can beryllium seen in the north cerebral hemisphere, while the southern lights is found in the southern cerebral hemisphere.
While the best places to witness the aurora are concentrated close to the polar regions, the aurora borealis can sometimes be seen in the UK. The further northbound you are the to a greater extent probably you are to see the display, but in the past the northern lights hold been seen as far south as Cornwall and Rockwell Kent.
Lancaster University's Department of Physics runs a website titled AuroraWatch UK, which estimates the likelihood of an aurora being panoptical based on geomagnetic activity. Follow the squad's Twitter chronicle to see the latest UK alerts.
The conditions brawl still need to be right however. Dark and clear nights, rather with little idle defilement, offer the best chance of eyesight the dawning.
Do other planets have aurorae?
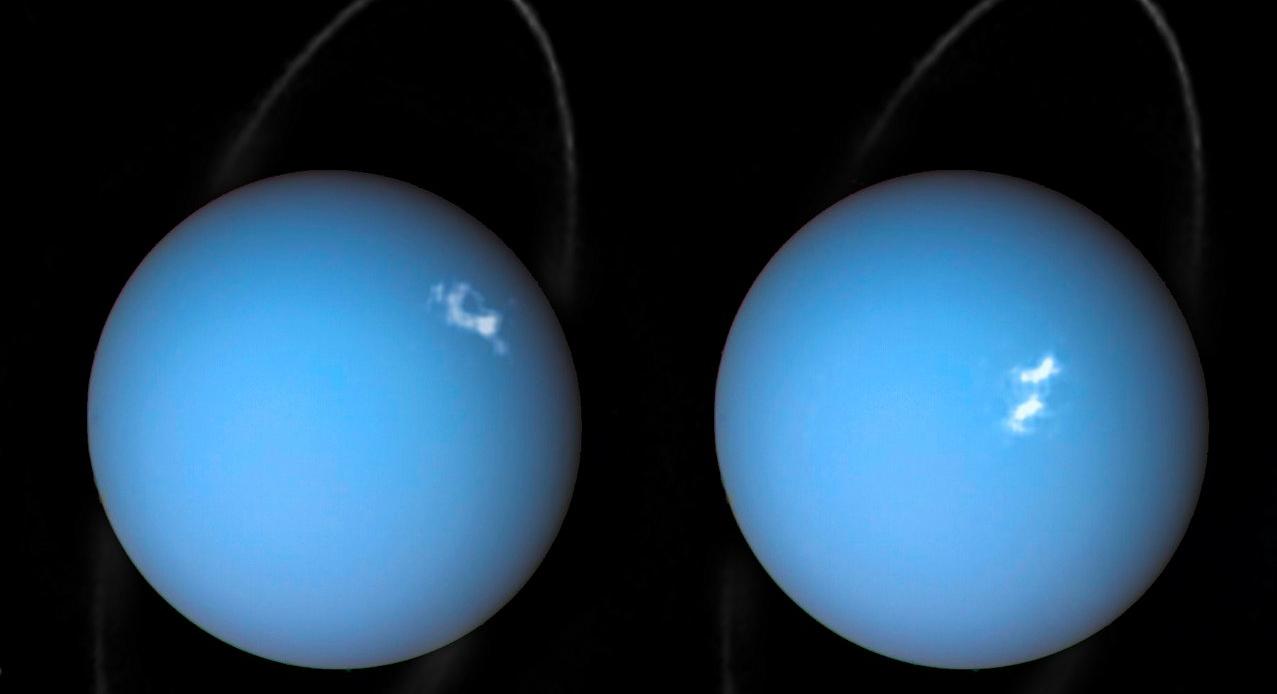
Any planet with an atmosphere and magnetic field is likely to throw aurorae. Scientists have captured incredible images of aurorae along Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
Aurorae happening Mars have got also been seen, but atomic number 3 the 'Red Planet' does not have a global magnetic field, aurorae behave other than and appear to be out-of-the-way more general.
What are solar flares and how do they affect the morning?
The aurora is a very dramatic case of the shipway in which solar activity affects the Earth.
Solar flares are like large explosions happening the surface of the Sun in which streams of charged particles are emitted into space. It typically takes two days aft the flare is seen connected the Insolate for the particles to reach Earth. Upon their arrival, these particles can result in break of day activeness.
What are geomagnetic storms?
Intense first light displays are generated following massive explosions on the Sun known as 'coronal multitude ejections'. These explosions release clouds of hot plasma containing billions of lashing of material travelling at about two million miles per hour. When the clouds reach the Worldly concern, they interact with the Earth's magnetised field to cause events called geomagnetic storms.
The Sun's activity fluctuates, with activity reaching a peak every 11 years. The last time star activity peaked was in 2014, and the pedal is now stretch its minimum. However, solar bodily function is predicted to rise again finished to the mid-2020s.
Unheeding of the Sun's activity, aurorae seat still occur at whatever time and observers in commanding latitudes should always watch for them.
Main image: Goðafoss Flow by Larryn Rae, Astronomy Photographer of the Year 2021
how does the sun produce the aurora on earth
Source: https://www.rmg.co.uk/stories/topics/what-causes-northern-lights-aurora-borealis-explained



Posting Komentar untuk "how does the sun produce the aurora on earth"